 |
| Quadriceps muscle strain |
The quadriceps muscle strain is an injury to the quadriceps muscles, which are the large muscles in the front of the thighs. The quadriceps muscles help you extend your knee and are important for running, jumping, and other athletic activities.
The quadriceps muscle strain is a strain, or a tear, of one or more of the quadriceps muscles. The exact cause of a quadriceps muscle strain is often difficult to pinpoint, but certain activities seem to increase the risk of this injury.
This injury is usually due to an overstretch of the muscle, often at the same time as a jerky muscle contraction or repetitive working overload. The quadriceps muscles, which consist of four muscles, can be overstretched by continuous muscle contractions of the knee.
Acute muscle strain was commonly seen in sports competitions such as soccer, rugby, and football. These sports require forceful muscle contraction of the quadriceps to control knee movement. Sudden jerky forces across the muscle contraction can lead to strain injury. Overstretching of muscle can also cause strains. Out of four quadriceps muscles, the rectus femoris is most frequently strained. There are too many factors responsible for frequent strain injury.
Quadriceps muscle Anatomy :
The Quadriceps femoris muscle is worked as a hip flexor and a knee extensor. It is located in front of the thigh (the anterior compartment).
This muscle group is composed of 4 muscles:
- Rectus femoris
- Vastus lateralis
- Vastus medialis
- Vastus intermedius
The Rectus femoris is the only 2 joint muscle working in both Hip flexion and knee extension. The other 3 muscles are primarily working as knee extensors. The rectus femoris is located in the most superficial part of the quadriceps and it crosses both the hip and
knee joints, thus also making it more vulnerable to stretch-induced strain injuries.
The most common sites of strains are mostly at the junction of the muscle tendon just above the knee.
What are the causes of Quadriceps muscle strain?
The quadriceps muscles are located at the front of the thigh and are often injured mostly during sports or overuse. Quadriceps strain can frequently occur in sports where jumping, Kicking, sudden stopping, running and jerky knee movement require. However the quadriceps muscles are one of the strongest muscle groups involved in supporting the body’s movement while playing a sport, a quadriceps muscle strain is commonly seen.
A consequence of repetitive overuse of Quadriceps muscles causes muscle fibers to become inflamed and may lead to a partial tear.
Grades of quadriceps strain :
Quad. Strains are divided into 3 grades depending on the injury level, Mild injury counted grade 1 while more severe injury counted Grade 2 and a complete or near-complete tear of the muscle is counted as a grade 3 injury.
Quad. Grade 1 Injury :
Symptoms of grade 1 injury mainly are pain and spasm at the front of the thigh with a general feeling of tightness, you feel mild pain when you walk, sit to stand, and squatting-related activities such as stair climbing and standing from the ground. A lumping gait is also associated if you do not take enough rest. you need 2 to 3 weeks rest.
Grade 2 Injury :
You may feel a sudden sharp pain when walking, running, jumping, or kicking an object. Lumping gait with Pain will make your walking difficult and swelling or mild bruising may be noticed. The pain and muscle spasm at the front of the thigh with Knee swelling and sometimes ankle swelling in the evening if you do not take rest. Knee extension with resistance is painful and your knee bending is also painful and sitting to stand is also difficult. you need rest for 1 month
Grade 3 Injury :
Quad strain Grade 3 Injury are mostly severe injury and symptoms are Pain and spasm at the front of thigh even during rest. You will be unable to walk without the help of crutches and unable to take weight on the affected limb. Knee and ankle swelling will appear immediately and significant bruising within a few hours. Knee movement will be painful and your front thigh area is seen as a bulge. You will require complete rest for nearly 6 to 12 weeks.
Symptoms of Quadriceps muscle strain :
Most common Quad. strain Symptoms are:
- Knee and Ankle swelling mainly at the evening in the Grade 3 Injury Swelling present within few Hours of Injury
- Knee pain with Muscle Pain and spasm at the Front of the thigh
- loss of strength (Muscle wasting)
- difficulty moving the leg - Knee bending is painful
- Lumping Gait and in severe Grade 3 injury require support
- The front of the thigh is Bulging if not taken enough rest and Medication.
Differential Diagnosis :
- Quadriceps Contusion
- Jumper's Knee
- Femoral Neck Stress Fracture
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
Diagnosis:
Your doctor will discuss with you your Medical history and the injury-related information. They will also discuss your symptoms and examine the thigh for tenderness and bruising and perform examination if required.
Your Doctor also checks knee movement mainly the range of motion for that they may ask you to bend and straighten your knee. To verify Diagnosis, an x-ray or other diagnostics may be prescribed to determine the grade of the injury mainly MRI or CT Scan.
Quad. Muscle strains are graded depending on their degree of severity, 1 being mild and 3 being severe injury. A Grade 1 strain can heal mostly quickly, while a Grade 3 strain might take a longer period of time.
Treatment of Quadriceps muscle strain
Most muscle strains can be treated with the use of the RICE principle (RICE stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation) while in Chronic case and Garde 1 Injury also you can use MICE Principle (MICE stands for Movement, Ice, Compression, and Elevation).
Rest: Take enough rest from the activity that caused the pain(Avoid Painful activity). Your doctor may recommend that you use crutches to avoid putting weight on the leg.
Ice Pack: Use cold packs for 10-15 minutes at a time, 2 to 3 times a day. Do not apply ice directly to the skin.
Compression: To reduce swelling, lightly wrap the injured area in a soft bandage or ace wrap, you can use a crepe-Bandage or Knee Cap.
Elevation: To reduce knee and Ankle swelling, raise your leg up higher than your chest, you can use Pillow for under your Ankle and Knee in a fully supported position 3 times a day.
Your doctor may prescribe a Medicine mainly NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), such as Aceclofenac or Diclofenac, for symptomatic pain relief. As the pain and swelling relieved, You recommended Physical therapy to improve range of motion and muscle strength. The exercise should be at full strength and pain-free before you start sports. This will help prevent re-injury.
Knee Positioning :
When a quadriceps muscle strain occurs during playing sports or during a training session, it is important to start treatment immediately. As early as possible following the injury, you need to keep the knee of the affected leg immediately in 120° of flexion.
This helps to avoid the potential risk of muscle spasms, reduces internal hemorrhage, and minimizes the risk of developing other complications such as myositis ossificans.
However, this can be done by placing the patient in a hinged knee brace at 120° of knee flexion or using crepe-bandage to maintain this position of flexion. If you keep the knee in a full extension position, the healing will be slower and more painful because the muscles will start to heal in a shortened position, you also need a longer rehabilitation process.
Physiotherapy Treatment :
Physical therapy treatment depends on the grade of injury, symptoms. Treatment is mainly Pain relieving Electrotherapy Modalities such as Interferential Therapy(IFT), Ultrasound Therapy(US), TENS, Use of Hot and Cold Pack.
The goal of Treatment :
- Relieve Pain with The Help of Pain relieving Electrotherapy Modalities.
- Maintain Range of Motion exercise (ROM)
- Stretching Exercise of Tight muscles
- Strengthening exercise of weak muscles
- Maintenance of aerobic fitness
- Proprioceptive exercises
- Functional training
Stretching exercise:
Stretching Exercise should be done carefully until you feel the gentle stretch and must be pain-free. Various stretching exercise techniques can be used mainly passive, active-passive, dynamic, and proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation stretching. However, ballistic stretching is avoided due to the risk of re-injury of muscle fibers. If it is pain-free, stretch the quad muscles gradually.
Static quadriceps stretching exercise:
This can be done in either standing or in a side-lying position. Flex the knee of the affected leg towards your buttock until you can feel a gentle stretch on the front of the thigh. To increase the stretch, extend your hips backward. Hold for 10-20 seconds and repeat 2 to 3 times. Do 2 to 3 times a day.
This stretching exercise will affect mainly the rectus femoris and Iliopsoas muscles. To do this exercise Take a Kneeling position with a normal knee on the soft mat while the affected foot is out in front with the knee bent. Gradually try to extend the hip (your hips forwards) and keep the back straight. You should feel a gentle stretch at the front of the hip and top of the thigh. Hold for 10-20 seconds, repeat 2 to 3 times, at least 2 times a day.
Strengthening exercises:
Strengthening exercise can start within the First week, initially, you start an only active exercise and must be pain-free.
Initially, you can start Isometric or static exercises and then progress to active exercises with gradual progress with resistance thera-band or you can use of weight cuff and finish with sports specific running and exercise training sessions.
Static quadriceps exercise: |
| Static quadriceps exercise - SQE |
This quadriceps contractions exercise is done to keep the knee fully extended position with first day 10 to 15 repetitions and 2 times a day. As you progress, you can increase repetitions. As knee range of motion improves, you may discontinue isometrics when the patient can sit comfortably. you can start active knee extension exercise.
Straight leg raises exercise:
Take a supine lying position on a soft mat, with a normal leg slightly flexed position. Gradually elevate the affected leg off the floor and keep the knee fully straight. Hold for 4 to 6 seconds and gradually lower the leg. Repeat 8 to 10 times on the first day and increase the repetition as you improve. This exercise can be done daily 2 to 3 times daily. Progression of exercise by increasing holding time and the number of repetitions.
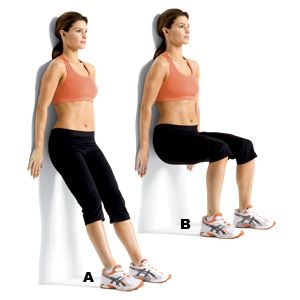
Take a standing position with Bodyweight supported by Wall, From your standing position, gradually lower your body down and hold for 5 to 10 seconds. As you improve, you can lower more and also increase Holding time while at the same time your Neck, Hip, and Back are supported with Wall. Exercise must be pain-free. Perform initially 2 sets of 5-10 seconds holds once per day. Gradually 2 times and 10-20 seconds depends on your stamina.
Step-ups exercise :
You can start with a box height table or use a stair that is comfortable for you to step upon. Be sure to keep your knee in a neutral position with your second toe. Put your affected leg on the first stair or table Step up while your back is in a neutral position
 .
.
Be sure to use the gluteal muscles and fully lock the knee after stepping up. Return gradually back down to the ground. You should be on the slow eccentric (lowering) back to the ground for 2second up and 4 seconds down. You can do initially 2 sets of 8-10 repetitions on the first day.
Exercise must be pain-free.
Gradually increase repetitions and set as you improve, as you progress after the week you can use stairs for more steps to up and down.
Exercise for Sportsmen / Athletes:
This exercise started when all symptoms are completely gone away mostly after 1 month, However, it may vary depending upon the grade of injury and symptoms.
- Full strength training with pain-free and increase repetition and sets of the exercise with in-between rest periods.
- Full range of motion exercise (ROM) - must be pain-free
- Use of Athlete sport-specific exercise programs and movements at competition speed with caution - pain-free exercise.
- Isokinetic strength training should be done with a concentric and eccentric form of exercise training.
- Improve 120° of knee flexion with hip extended to maintain full length of Rectus femoris
Conclusion
Quadriceps muscle strain mostly occurs in sports competitions such as soccer, rugby, and football. These sports regularly demand high-intensity knee movement in which sudden forceful eccentric contraction of the quadriceps during regulation of knee flexion and hip extension.
Higher intensity movement across the muscle-tendon units with eccentric contraction can lead to muscle strain-related injury. Over passive stretching or activation of a maximally stretched muscle can also cause muscle strains during a training session. The rectus femoris is most frequently strained as compared to other quadricepsConclusisozz
Quadriceps muscle strain mostly occurs in sports competitions such as soccer, rugby, and football. These sports regularly demand high-intensity knee movement in which sudden forceful eccentric contraction of the quadriceps during regulation of knee flexion and hip extension.
Higher intensity movement across the muscle-tendon units with eccentric contraction can lead to muscle strain-related injury. Over passive stretching or activation of a maximally stretched muscle can also cause muscle strains during a training session. The rectus femoris is most frequently strained as compared to other quadriceps







No comments:
Post a Comment