|
| Home Visit Physiotherapy treatment |
The Advance treatment of Knee Pain / neck pain / Shoulder pain is physiotherapy. Best physiotherapists working in Physiotherapy clinics, hospitals, community centres etc. You can even get physiotherapy services at home in Ahmedabad for your convenience.
You can find competent and experienced physiotherapists at SamarpanPhysiotherapy Clinic. We are a chain of Physiotherapy clinics that offer top quality Physiotherapy services in the east, south, west and north parts of Ahmedabad.
We offer services in physiotherapy field in our state-of-the-art clinics from 2005. We even offer physiotherapy services at home in east Ahmedabad and provide Advance Rehabiliation Care according to the need of each patient.
Get the Best of Physiotherapist at Home Visit Treatment :
People who suffer from Joint Pain eg. Knee Pain/Back Pain , the best treatment for them is physiotherapy at home in Ahmedabad. Some people suffer from Paralysis and that limits their mobility and unable to visit the center. Don't worry if you cannot visit Samarpan Physiotherapy clinic for physiotherapy treatment. You can get physiotherapy treatment at home as well by contact us. You can contact our physiotherapist directly for an appointment. Before choosing a physiotherapist, ask about the area of specialization of the physiotherapist and only then appoint him.
What To Expect in Physiotherapy at Home in Ahmedabad ?
On the first day of your meeting with physiotherapist at your home, he /she would ask you a few questions associated with your health to take assess you, to provide you better treatment. You must be specific and answer all questions with clarity. After taking your medical history, the physiotherapist would carefully and thoroughly examine the area of pain and immobility. You are expected to honestly answer whatever questions the physiotherapist asks you during the assessment. After the assessment, he would advise a treatment plan for you. The treatment would include exercise and medicine for speedy recovery.
Get the Best Specialists for Physiotherapy At Home in East Ahmedabad :
After a careful and thorough physical examination, the physiotherapist would be able to diagnose your condition. On the basis of his diagnosis, he/she would chalk out a treatment plan which would help you in recovering soon and improving your health goal. The success of the treatment depends on accurate diagnosis, treatment plan as well as co-operation from the patient. During the entire process of the physical examination, the patient is expected to co-operate and answer all questions honestly. During the treatment, the patient is expected to work out regularly, maintain a healthy diet and sincerely do the exercises the physiotherapist teaches you.
EXERCISES THE PHYSIOTHERAPISTS SUGGESTS TO PATIENTS :
If you want to avail services in physiotherapy at home in Ahmedabad, you may call Samarpan Physio. to fix an appointment with one of our physiotherapists. Here are some general and specific exercises that the physiotherapist would teach you and instruct you to do at home.
1. General Strengthening Exercise :
General Strengthening Exercise Helps to improve stamina and make you strong enough to make your day to day activity easy. Joint Pain can discourage you to avoid exercising but the physiotherapist would urge you to exercise daily. Bed rest would only aggravate your pain and weaken your muscles. To increase your overall endurance or body strength, you must walk or jog for 5 days in a week.
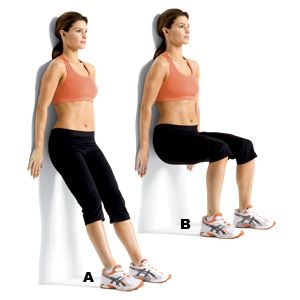
2. Specific Exercise
‘Pelvic Tilt’ Exercise: You need to lie down on supine position on a soft mat with the feet flat on the firm surface and knees bent. You should tuck the stomach inwards by pulling the lower part of the abdominal muscles and then hold your back during breathing easily out and in.
Back Extension Exercise : You need to lie down on supine position on a soft mat with your entire weight exerted on the forearms. While lying down lean on the elbows and stay in that position for 5 to 10 seconds. During the exercise ensure to relax your lower back completely.
Conclusion :
Physiotherapy treatment is the worldwide highly selected option for all types of body pain eg. Knee pain, Back Pain and Paralysis. It helps in improving your Bad posture, strengthening your weak muscles and overall improve mobility of your body and also helps reducing pain. Contact Samarpan Physio and make an appointment with a Best physiotherapist right away and get the best physiotherapy treatment at home in Ahmedabad.
CONTACT US :
Nava Naroda Physiotherapy Clinic Address :
Samarpan Physiotherapy Clinic
- 11, Vedant Bunglow, Opp.Radhe-2 Bunglow,
- Near. Haridarshan Char Rasta, Behind.Shalby Hospital
- Near. Fortune Circle, New India Colony Road
- Sardar Patel Road, Nava Naroda, Ahmedabad.
Dr. Nitesh Patel – Physiotherapist.
Mo No. : 09898607803
Dr. Varsha Patel – Physiotherapist.
Dr. Pankati Patel – Physiotherapist.
Timing :
Morning : 8 :30 am to 1 :00 pm
Evening : 4 :00 pm to 8 :00 pm
Sunday : 9 :00 am to 12:00 pm
Our Other Branch Clinic Address :
Mobile Physiotherapy Clinic
- B-01, Jagatnagar Society, Opp.Shaktidhara Society,
- India Colony Road, Tollnaka, Bapunagar
- Ahmedabad.
Dr. Nitesh Patel – Physiotherapist.
Mo No : 09898607803
Dr. Anjali – Physiotherapist.
Dr. Sumaiya Qureshi – Physiotherapist.
Dr. Pal Rawal – Physiotherapist
Dr. – Physiotherapist.
Website : https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in
Timing :
Morning : 9 :00 am to 1 :00 pm
Evening : 4 :00 pm to 8 :00 pm
Sunday : 9 :00 am to 12:00 pm